CSO Synthesis of the Global Mechanism Report on the Implementation of the Voluntary Targets for Land Degradation Neutrality and Related Implementation Activities.
Document ICCD/CRIC(19)/2 to be revised at the 19th session of the Committee for the Review of the Implementation of the Convention (CRIC).
____________________
- Background information on the process of implementation of Land Degradation Neutrality
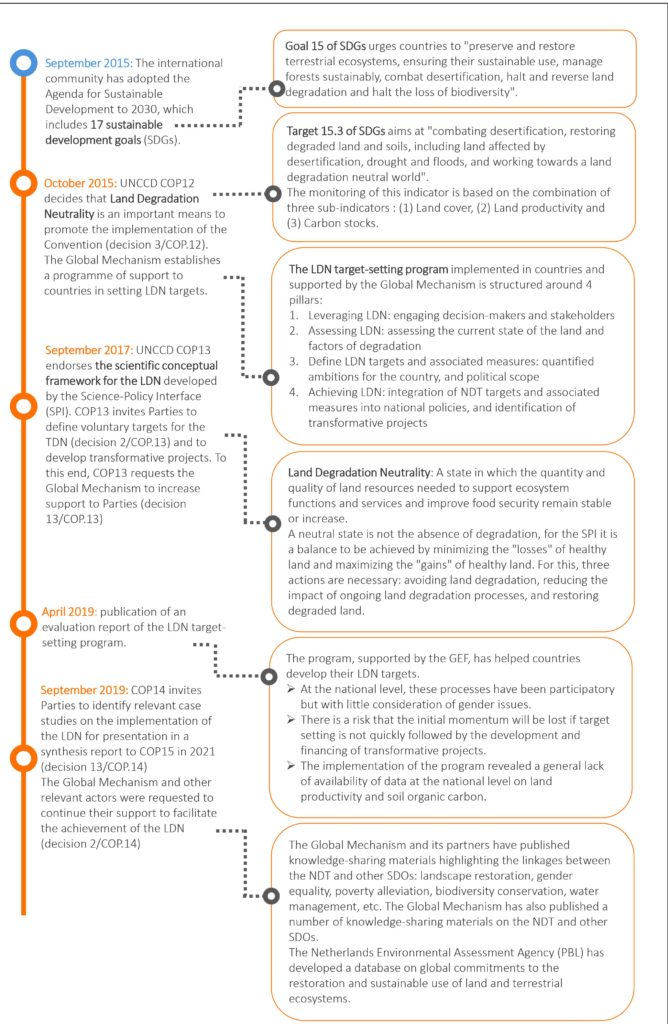
- Update on the implementation of the Land Degradation Neutrality target-setting program as of October 15, 2020
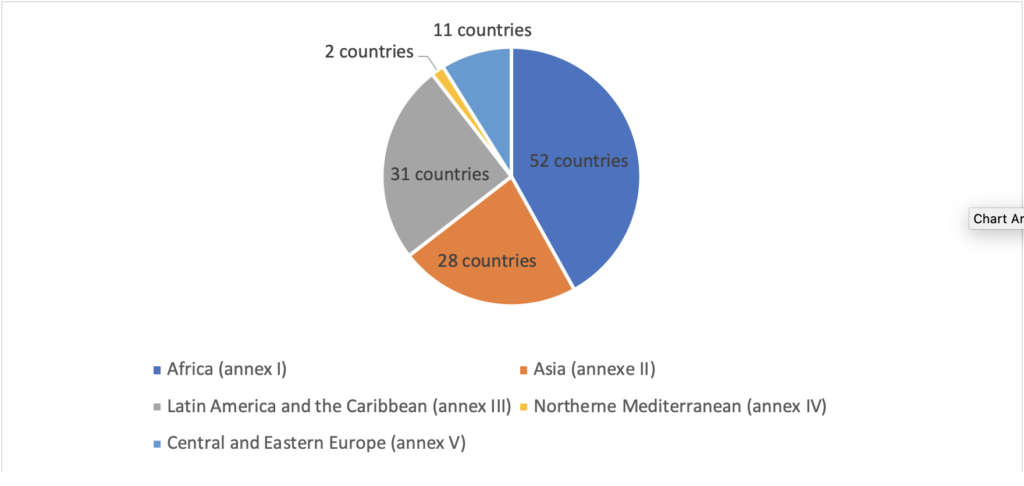
124 countries* participated to the LDN target-setting program
102 countries have defined and validated voluntary LDN targets and corresponding measures
66 countries have formally adopted their LDN and delivered a high-level note on the issue
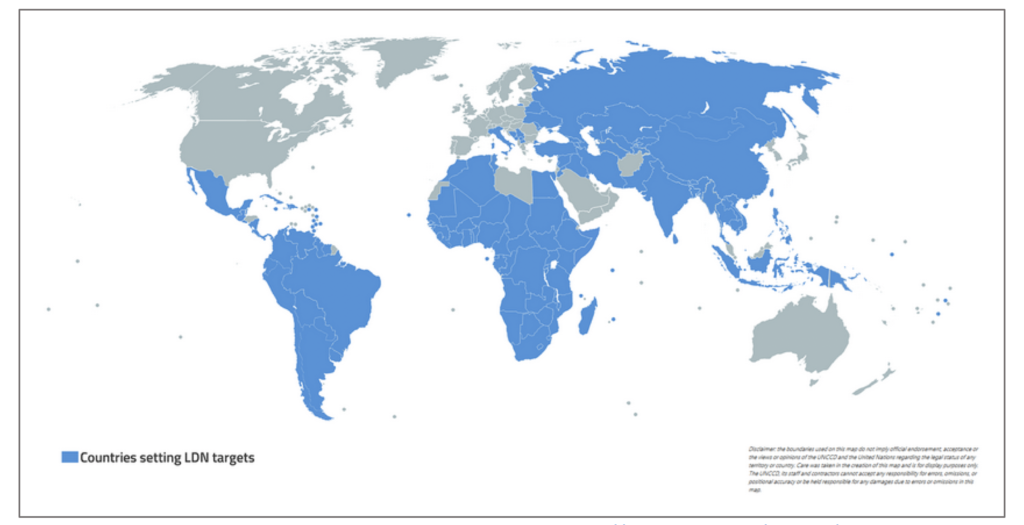
* Update 2021 : 127 countries have set LDN targets https://www.unccd.int/actions/ldn-target-setting-programme
These LDN targets set between 2017 and 2020 translate into commitments to restore 450 million hectares of degraded land, in addition to the 250 million hectares identified as nationally determined contributions, and approximately 90 million hectares identified for restoration in the national action plans developed under the Convention on Biological Diversity.
| Comments: - The report lacks details on the characterization in the countries of these commitments (mapping of areas to be restored, etc.) - The report mainly mentions commitments for land restoration. It does not specify whether commitments for the reduction and avoidance of land degradation are also specified. - The report lacks details on the degree of fulfillment of these commitments. |
- Global Mechanism support for the development and implementation of transformative projects and programs to achieve Land Degradation Neutrality targets
Following the definition of the voluntary LDN targets, countries are invited to identify and develop transformative projects and programs to implement their commitments. In response to countries’ request, the Global Mechanism offers support in the early stages of project development to prepare good quality concept notes that can be submitted to institutions such as the Green Climate Fund and the Global Environment Facility.
The report states that the Global Mechanism’s support was provided to countries that applied to a call for expressions of interest, and were selected on the basis of the following criteria:
- Technically developed and validated LDN targets
- Submission of a note describing the project idea consistent with the guiding principles of the scientific conceptual framework of the LDN
- Identification of a possible source of funding
The Global Mechanism’s support to countries is provided through its technical team and through the provision of a national consultant for a period of 8 to 12 months, dedicated exclusively to the development of project proposals in collaboration with national and other stakeholders.
The report notes that it takes an average of 12 to 24 months for a project idea note to become a concept note approved by a funding partner such as the GEF or the GCF.
Since the beginning of this program to support the development of transformative projects and programs to October 15, 2020:
52 countries have participated and submitted 55 national projects: 14 concept notes have been developed, 11 notes are under development, 30 notes are in draft.
38 countries have proposed 6 regional projects: 5 concept notes are developed and 1 note is under development.
- The list of participating countries is presented in the annex at the end of document ICCD/CRIC(19)/2.
9 projects have been selected for funding, including 7 national and 2 regional.
| Comments : - The report does not give details on the content of the projects set up, their areas of intervention, type of activities and operational portage. - The sources of financing identified for these LDN projects are the GCF and the GEF. The report does not mention the LDN Fund once. |
- Capacity-building actions led by the Global Mechanism, other relevant institutions and bodies of the Convention.
The report outlines a series of actions undertaken to build the capacity of various stakeholders on the achievement of LDN. These actions are expected to continue.
- Summary of the overall conclusions of the report
While the GM’s support to countries in setting the LDN targets is considered effective, this process depends on the active engagement of the appointed UNCCD focal points in each country, and the political commitment of countries to the LDN is ultimately manifested through the adoption of the targets at a high level (ministers, inter-ministerial bodies, councils of ministers or heads of state). The process of defining the LDN targets has identified areas of capacity building that countries need to address. These include in particular the capacity to conduct monitoring and evaluation of the LDN which relies heavily on the processing of geospatial data.
The Global Mechanism’s support to countries in developing transformative projects and programs has created an important pipeline of project ideas, and the report highlights the technical and financial needs of countries to finalize project development.
- Summary of recommendations provided in the report
These recommendations will be considered by the Parties at the CRIC, which may decide to forward them to the COP for further consideration, which may then lead to decisions for implementation of these recommendations.
Recommendations to Parties:
- Complete their process of setting voluntary NDT targets and adopt their targets at the highest political or institutional level.
- Regularly review and update their NOW targets, ensuring that they are quantitative and area specific.
- Develop systems to monitor progress in preventing, reducing and reversing land degradation.
- Increase the coherence of their process for setting voluntary NDT targets or harmonize it with other relevant ongoing processes.
Recommendations to the Global Mechanism and the UNCCD Secretariat:
- Facilitate the establishment of an enabling environment for the review and refinement of voluntary LDN targets and the integration of the LDN into relevant land-use planning processes and frameworks.
- Support capacity development for data collection and analysis, quantitative representation, geospatial mapping and monitoring of the LDN targets, land use monitoring through on-line platforms and reporting.
- Establish effective partnerships to accelerate the development of bankable projects and large- scale investment programs by accessing relevant funding sources, including the Adaptation Fund, the GCF, the GEF, the multilateral development banks, other bilateral and multilateral sources, and private sector funding.
- Continue to support capacity building for the development and financing of projects (public and private) and the design and implementation of transformative gender-sensitive projects and programs.